Reliable, safe, and affordable personal and commercial transportation is vital to U.S. economic development, but transportation’s energy intensity and harmful emissions must be reduced. We focus on the technology, engineering, and policy breakthroughs needed to do this.

Harnessing the power of supercomputing and structural methods, the Materials Project provides open, web-based access to information on known and predicted materials as well as powerful analysis tools to inspire and design novel materials.
A multidisciplinary team focused on a diverse portfolio of advanced energy conversion technologies with the goal of providing the tools necessary to create and sustain a cleaner energy system.
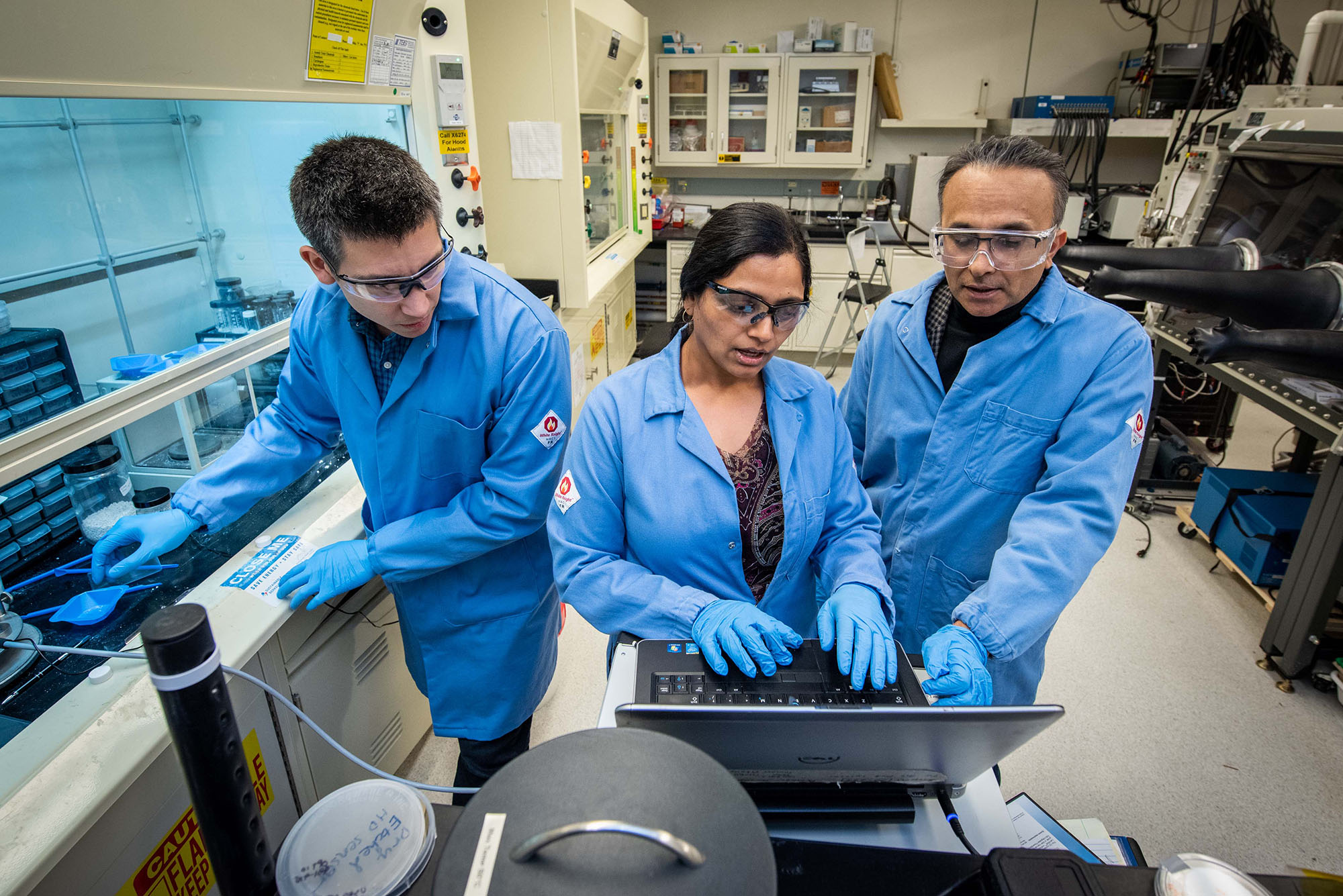

A science-to-systems lab conducting research in manipulating matter at nanoscale dimensions to improve a multitude of thermal, solar, and electrochemical energy devices, including batteries.

Advancing the efficiency, power, and durability of hydrogen fuel cell engines for heavy-duty vehicles to enable a fleet of clean, emission-free long-haul trucks.

Building on 70 years of scientific leadership in energy storage research, Berkeley Lab’s Energy Storage Center is advancing solutions that affect the evolving grid, transportation, industrial sectors, buildings, and resilience.

Collaborating with the Institute of Transportation Studies at UC Berkeley to develop new science, engineering tools, and technology to support a more energy-efficient transportation system.

Berkeley Lab conducts unbiased analysis to evaluate the cost implications and environmental impacts of a wide range of energy technologies and strategies to support decision-making by groups.

Arman Shehabi has over 15 years’ of experience measuring and modeling the potential energy, economic, and air pollutant impacts associated with the large-scale adoption of clean energy policy and technologies for buildings and manufacturing, with extensive research focused on the information and communication technology (ICT).

Black is the Grid Integration Group Leader at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. Doug has over 20 years of research experience and is currently, and has been, the principal investigator for many successful microgrid and vehicle-to-grid integration (VGI) demonstration projects.

Spurlock is a research scientist and a deputy department head in the Sustainable Energy and Environmental Systems Department. Spurlock has a leadership role in the Sustainable Transportation Initiative and also leads the Economics Research sub-team within the Energy Efficiency Standards Department.
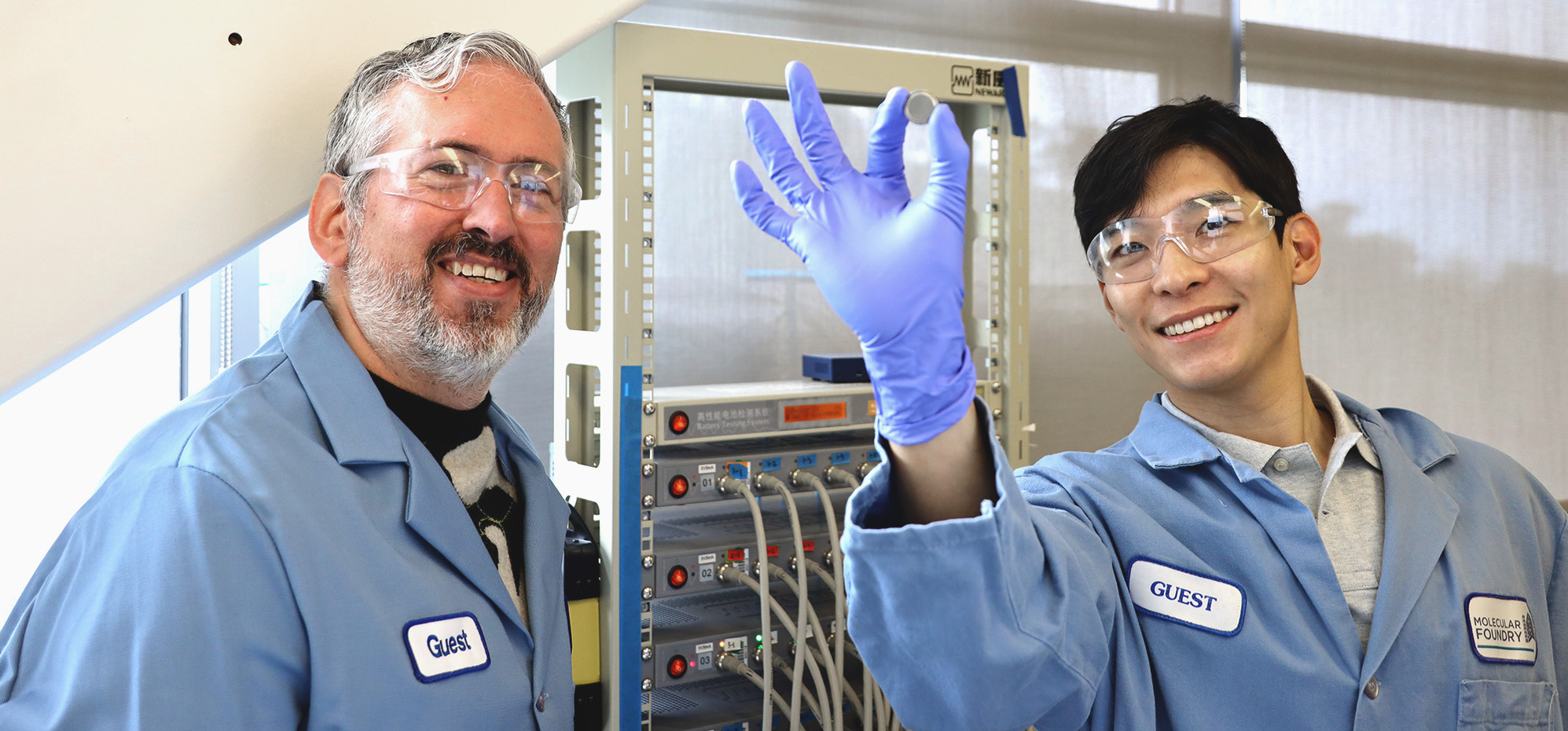


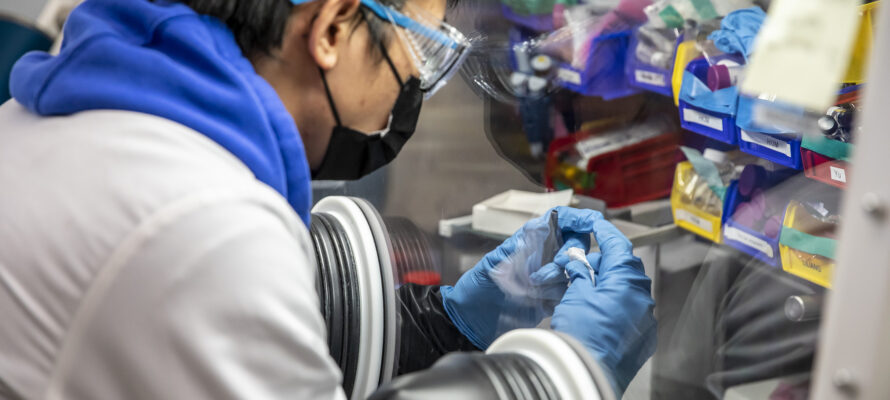
In a new study, a team of researchers led by Berkeley Lab used a bioscience technique to study the intricate interactions within the anode, cathode, and electrolyte of electric aircraft batteries. One of the most significant findings was the discovery that certain salts mixed into the battery electrolyte formed a protective coating on cathode particles, making them far more resistant to corrosion, thereby enhancing battery life.
By harnessing the power of AI and machine learning, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory scientists are developing a tool that predicts properties of high-potential, bio-based molecules and fuels, paving the way for cost-effective and sustainable jet fuel production. This innovation offers a promising short-term solution to reduce emissions.






