Berkeley Lab has capabilities in all aspects of biomanufacturing. Our teams of synthetic biologists, biochemists, and process engineers collaborate with academic groups and companies to invent innovative solutions and advance them to market readiness – changing what’s possible in fuels, therapeutics, food, personal products, and high-performance materials.

Artificial intelligence-driven design/synthetic biology
Using machine learning and cutting-edge software programs to speed up the process of designing and engineering biological pathways for producing important compounds.
Genome engineering
Using advanced gene editing tools to engineer plants and microbes capable of producing valuable, sustainable bioproducts.
Sustainable biomanufacturing
Harnessing microbes to produce biofuels and bioproducts from waste streams and other feedstocks.
Scale-up
Developing and optimizing all phases of bioproduct manufacturing processes, from host organism design to product purification.
Techno-economic analysis
Developing publicly-available techno-economic models: a type of simulation that analyzes the financial and environmental outcomes of biomanufacturing processes based on the technology used and the chemical inputs, allowing researchers to design the most efficient and responsible “recipes” for large-scale production.
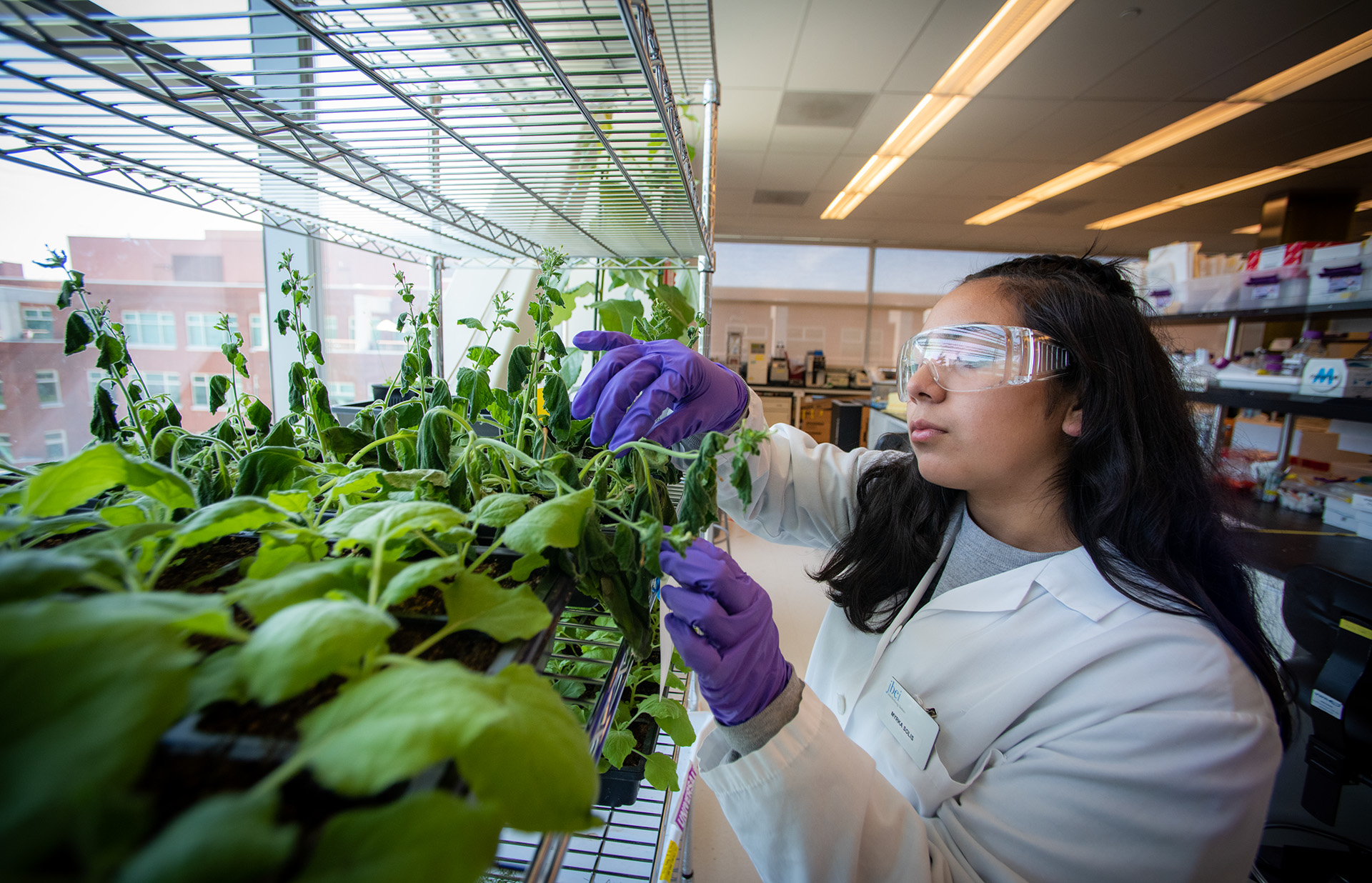

Inside the JBEI’s Emeryville laboratories, researchers are using the latest tools in molecular biology, chemical engineering, computational, and robotic technologies to transform biomass into biofuels and bioproducts.
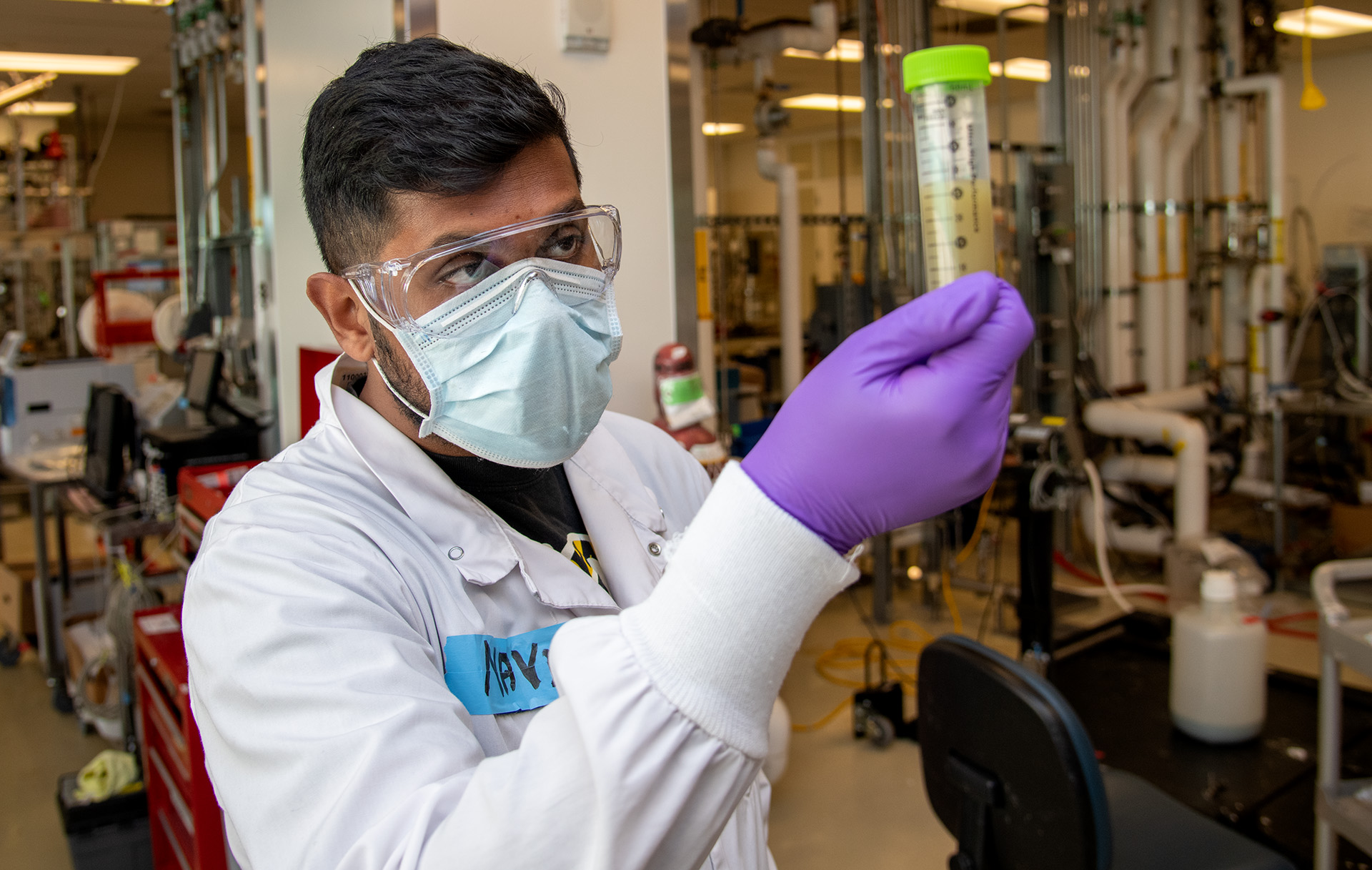

The ABPDU collaborates with academic labs, start-ups, and established companies to accelerate new biology-based products from early R&D to market readiness.
The Agile BioFoundry, a consortium of national laboratories dedicated to accelerating biomanufacturing, engineers biological systems to produce molecules at optimal yields, efficiencies, and costs.
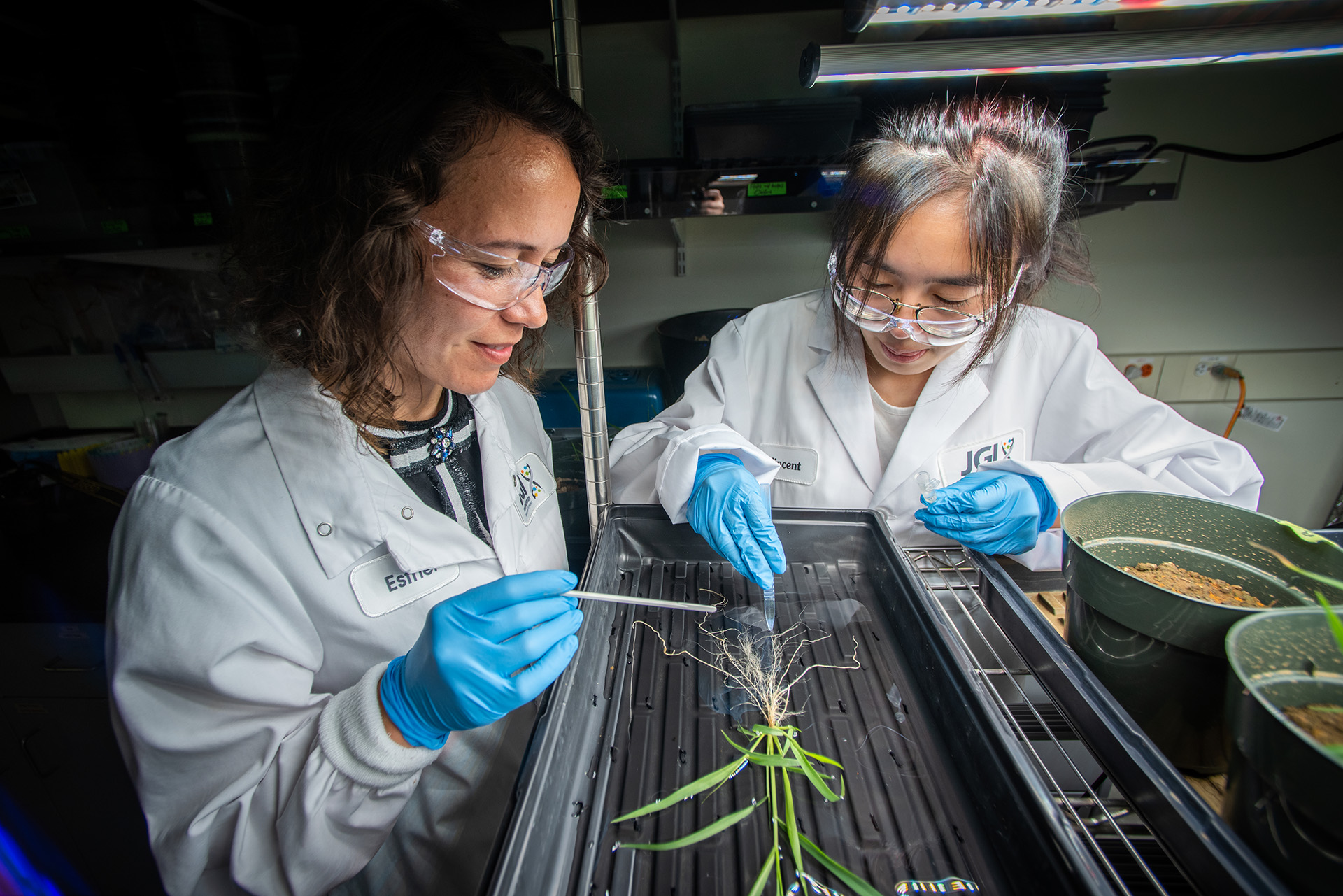

The JGI provides integrated high-throughput sequencing, DNA design and synthesis, cell metabolite analysis, and computational analysis that helps researchers engineer better biofuel plant species and microbes that convert tough plant matter into fuel precursors like ethanol.

This DOE Bioenergy Technologies Office-funded consortium focuses on research to transform CO2 and electrons into sustainable aviation fuels.

Empowers the research community to harness microbiome data exploration and discovery through a collaborative integrative data science ecosystem.

Berkeley Lab conducts unbiased analysis to evaluate the cost implications and environmental impacts of a wide range of energy technologies and strategies to support decision-making by groups.

Deepti Tanjore is Director of the Advanced Biofuels and Bioproducts Process Development Unit (ABPDU). Her research focuses on modeling the impact of bioprocess conditions on microbial heterogeneity and developing in-line analytical tools for real-time adaptation of process development in bioreactors.

Nathan Hillson's work has spanned the realms of the private (notably as co-founder and Chief Scientific Officer at TeselaGen Biotechnologies, Inc.) and public biotechnology sectors. He leads scientists and engineers whose domain expertise spans synthetic biology, metabolic engineering, microbiology, software engineering, and laboratory automation engineering.

Blake Simmons is the Director of Berkeley Lab's Biological Systems and Engineering Division and the Chief Science and Technology Officer at the Joint BioEnergy Institute. His research focuses on developing innovative science-based solutions that generate advanced biofuels and bioproducts produced from sustainable, non-food lignocellulosic biomass, plastic, gaseous, and mixed feedstocks.
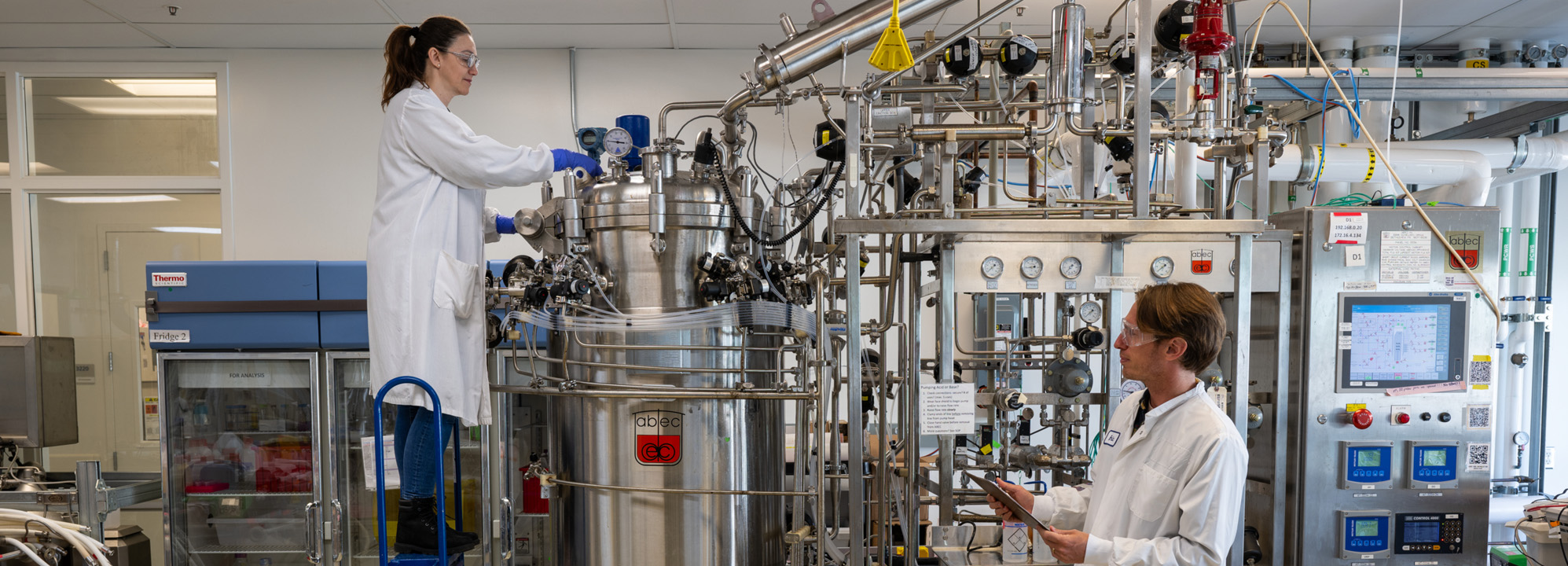

The Advanced Biofuels and Bioproducts Process Development Unit, or ABPDU, helps biomanufacturing companies scale up innovative biotechnologies and transition them to the marketplace. To date, ABPDU has collaborated with over 90 industry partners; many have set up their own labs or pilot plants, secured additional funding, and launched their own products as a direct result of working with ABPDU.
From revolutionary advances in fuels to everyday products like cosmetics, bioreactors are at the forefront of science discoveries. Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Biofuels and Bioproducts Process Development Unit is starting to explore self-driving bioreactors. Learn how they plan to advance the future of bioreactors with autonomous systems, equipped with AI-microscopy and advanced quantum sensors.
In this 9-minute audio interview, Deepti Tanjore, director of the ABPDU, discusses the resources that the facility and its staff offer to help bring bio-based products to market and train the next generation of scientists.






